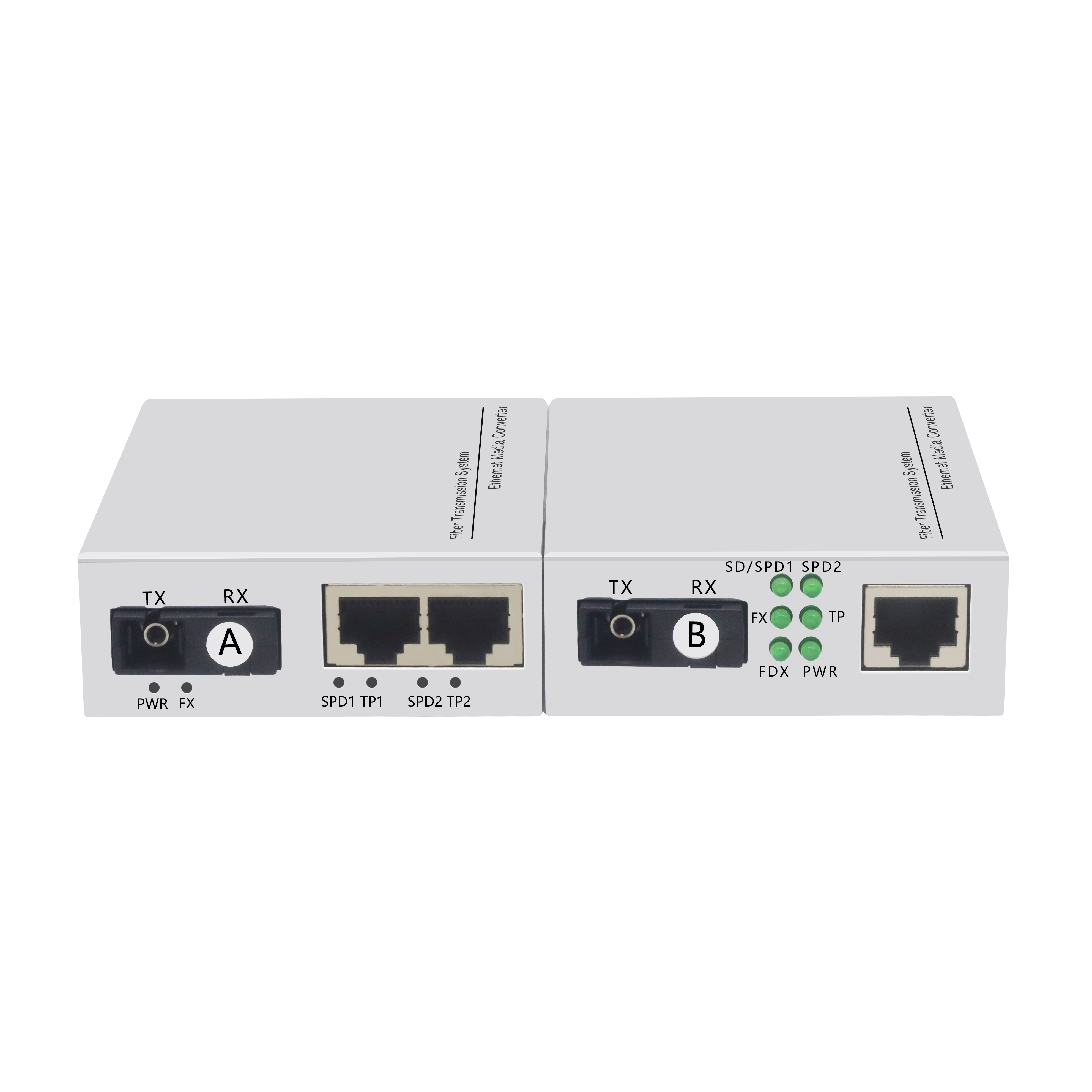
Gigabit fiber optic transceiver (one optical and two electrical)
product description:
TThis product is a gigabit fiber optic transceiver with 1 gigabit optical port and 2 1000Base-T(X) adaptive Ethernet RJ45 ports. It can help users realize the functions of Ethernet data exchange, aggregation and long-distance optical transmission. The device adopts fanless and low power consumption design, which has the advantages of convenient use, small size and simple maintenance. The product design conforms to the Ethernet standard, and the performance is stable and reliable. The equipment can be widely used in various broadband data transmission fields such as intelligent transportation, telecommunications, security, financial securities, customs, shipping, electric power, water conservancy and oil fields.
| model | CF-1022GSW-20 | |
| network port | 2×10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet ports | |
| Fiber port | 1×1000Base-FX SC interface | |
| Power interface | DC | |
| led | PWR, FDX, FX, TP, SD/SPD1, SPD2 | |
| rate | 100M | |
| light wavelength | TX1310/RX1550nm | |
| web standard | IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, IEEE802.3z | |
| Transmission distance | 20KM | |
| transfer mode | full duplex/half duplex | |
| IP rating | IP30 | |
| Backplane bandwidth | 6Gbps | |
| packet forwarding rate | 4.47Mpps | |
| Input voltage | DC 5V | |
| Power consumption | Full load<5W | |
| Operating temperature | -20℃ ~ +70℃ | |
| storage temperature | -15℃ ~ +35℃ | |
| Working humidity | 5%-95% (no condensation) | |
| Cooling method | fanless | |
| Dimensions (LxDxH) | 94mm×71mm×26mm | |
| weight | 200g | |
| Installation method | Desktop/Wall Mount | |
| Certification | CE, FCC, ROHS | |
| LED indicator | condition | meaning |
| SD/SPD1 | Bright | The current electrical port rate is gigabit |
| SPD2 | Bright | The current electrical port rate is 100M |
| extinguish | The current electrical port rate is 10M | |
| FX | Bright | Optical port connection is normal |
| flicker | Optical port has data transmission | |
| TP | Bright | The electrical connection is normal |
| flicker | The electrical port has data transmission | |
| FDX | Bright | The current port is working in full duplex state |
| extinguish | The current port is working in half-duplex state | |
| PWR | Bright | Power is OK |
How to choose a fiber optic transceiver?
Optical fiber transceivers break the 100-meter limitation of Ethernet cables in data transmission. Relying on high-performance switching chips and large-capacity caches, while truly achieving non-blocking transmission and switching performance, they also provide balanced traffic, isolation and conflict. Error detection and other functions ensure high security and stability during data transmission. Therefore, fiber optic transceiver products will still be an indispensable part of actual network construction for a long time. So, how should we choose fiber optic transceivers?
1. Port function test
Mainly test whether each port can work normally in the duplex state of 10Mbps, 100Mbps and half-duplex state. At the same time, it should be tested whether each port can automatically select the highest transmission speed and automatically match the transmission rate of other devices. This test can be included in other tests.
2. Compatibility test
It mainly tests the connection ability between the optical fiber transceiver and other devices compatible with Ethernet and Fast Ethernet (including network card, HUB, Switch, optical network card, and optical switch). The requirement must be able to support the connection of compatible products.
3. Cable connection characteristics
Test the fiber optic transceiver’s ability to support network cables. First, test the connection ability of Category 5 network cables with lengths of 100m and 10m, and test the connection ability of long Category 5 network cables (120m) of different brands. During the test, the optical port of the transceiver is required to have a connection capability of 10Mbps and a rate of 100Mbps, and the highest must be able to connect to a full-duplex 100Mbps without transmission errors. Category 3 twisted pair cables may not be tested. Subtests can be included in other tests.
4. Transmission characteristics (transmission loss rate of data packets of different lengths, transmission speed)
It mainly tests the packet loss rate when the optical fiber transceiver optical port transmits different data packets, and the connection speed under different connection rates. For the packet loss rate, you can use the test software provided by the network card to test the packet loss rate when the packet size is 64, 512, 1518, 128 (optional) and 1000 (optional) bytes under different connection rates. , the number of packet errors, the number of packets sent and received must be more than 2,000,000. Test transmission speed can use perform3, ping and other software.
5. The compatibility of the whole machine to the transmission network protocol
It mainly tests the compatibility of fiber optic transceivers to network protocols, which can be tested in Novell, Windows and other environments. The following low-level network protocols such as TCP/IP, IPX, NETBIOS, DHCP, etc. must be tested, and the protocols that need to be broadcast must be tested. Optical transceivers are required to support these protocols (VLAN, QOS, COS, etc.).
6. Indicator status test
Test whether the status of the indicator light is consistent with the description of the panel and the user manual, and whether it is consistent with the current status of the fiber optic transceiver.